Cheese, often celebrated for its rich flavor and variety, may now be gaining recognition for an unexpected health benefit: boosting the microbiome. A recent study has confirmed that cheese consumption can positively impact gut health, supporting the idea that it is not just a delicious treat but also a valuable ally in maintaining a balanced and healthy microbiome.
The Science Behind Cheese and Gut Health
The human gut is home to trillions of bacteria that play a vital role in digestion, immunity, and overall health. These microorganisms are collectively referred to as the “microbiome,” and maintaining a healthy balance of bacteria is crucial for well-being. Certain foods, such as fermented products, have long been linked to supporting gut health. Cheese, particularly aged or fermented varieties, is now recognized for its ability to promote a thriving microbiome.
The study, conducted by a team of researchers, found that cheese contains beneficial bacteria and compounds that can enhance the diversity and balance of gut microbiota. Specifically, the fermentation process involved in -making contributes to the development of beneficial probiotics, which are live microorganisms known to have positive effects on gut health.
How Cheese Benefits the Microbiome

The beneficial bacteria found in cheese are believed to influence the microbiome in several ways. These probiotics can help promote the growth of “good” bacteria in the gut, which in turn can suppress the growth of harmful bacteria. A balanced microbiome supports digestive health, strengthens the immune system, and may even have a role in mental health through the gut-brain connection.
Additionally, cheese is rich in nutrients like calcium, protein, and vitamins, all of which contribute to overall health. However, it is the live cultures and the fermentation process that make cheese particularly effective in boosting the microbiome. The study highlighted that not all such products are created equal in terms of microbiome benefits. Aged, raw, and blue cheeses tend to be more beneficial, as these varieties are often higher in probiotics.
The Impact of on Health
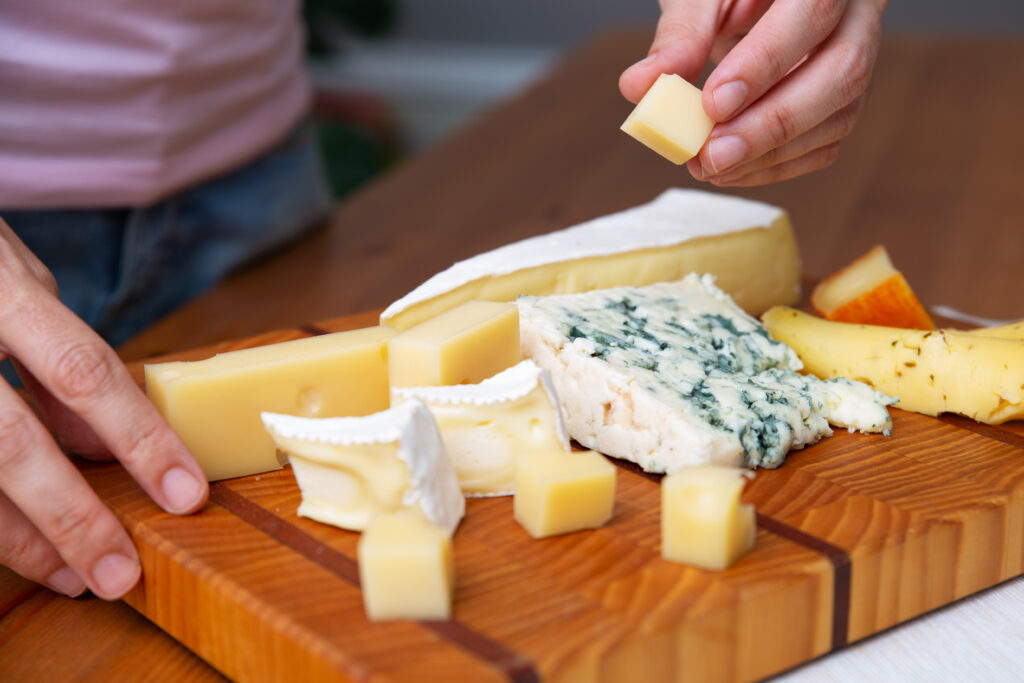

While cheese has long been admired for its taste, its role in gut health provides another reason to incorporate it into a balanced diet. However, it is important to consume cheese in moderation, as many varieties can be high in fat and sodium. For those looking to maximize the benefits of it without overindulging, choosing cheeses that are rich in probiotics, such as Gouda, cheddar, and Parmesan, may be the best options.
The study further suggests that including cheese as part of a diverse and well-rounded diet, rich in fiber, fruits, vegetables, and fermented foods, can offer optimal benefits to the microbiome. This approach may improve digestive health and overall wellness.
Conclusion
The research confirms what cheese enthusiasts may have suspected: cheese is more than just a tasty addition to meals—it can be a powerful tool in supporting gut health. The fermentation process, along with the presence of probiotics, makes cheese a unique and beneficial food for boosting the microbiome. So, the next time you enjoy a slice of your favorite dish, you can rest assured that you’re doing something good for your gut health.
Also Read: https://lifescienceinsights360.com/blog/role-of-grape-consumption-to-boost-muscle-health/