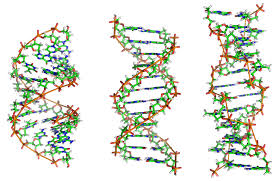
Deoxyribonucleic acid, commonly known as DNA, is the fundamental building block of life. It carries the genetic instructions necessary for the growth, development, functioning, and reproduction of all living organisms. Understanding DNA is crucial for comprehending the mechanisms of inheritance, evolution, and the functioning of living beings at a molecular level.
What is DNA?

DNA is a molecule composed of two strands that coil around each other to form a double helix. These strands are made up of nucleotides, which are the basic units of DNA. Each nucleotide consists of three components: a phosphate group, a sugar molecule (deoxyribose), and a nitrogenous base. There are four types of nitrogenous bases in DNA: adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G).
How DNA Works
The sequence of these nitrogenous bases determines the genetic information carried by a DNA molecule. The bases pair specifically: adenine pairs with thymine, and cytosine pairs with guanine. This pairing is crucial for the replication of DNA, allowing it to create identical copies of itself during cell division.
Role of DNA in Heredity
DNA plays a vital role in heredity, the process by which traits are passed from parents to offspring. Genes, which are segments of DNA, contain the instructions for making proteins, the molecules responsible for most functions in the body. These instructions are passed from one generation to the next, ensuring that offspring inherit traits from their parents.
Mutations, or changes in the DNA sequence, can lead to variations in these traits. Some mutations may have little effect, while others can lead to significant changes in an organism’s appearance, behavior, or health.
DNA and Evolution
DNA is also central to the process of evolution. Over time, mutations accumulate in the DNA of a population, leading to genetic diversity. Natural selection acts on this diversity, favoring traits that enhance survival and reproduction. Over many generations, these small changes can lead to the evolution of new species.
The Human Genome Project
One of the most significant scientific achievements in understanding DNA was the Human Genome Project. Completed in 2003, this international research effort successfully mapped the entire human genome, identifying all the genes present in human DNA. This groundbreaking project has paved the way for advancements in medicine, genetics, and our understanding of human biology.
Applications of DNA Research
Research in DNA has numerous applications in medicine, forensics, agriculture, and biotechnology. In medicine, understanding DNA has led to the development of gene therapy, personalized medicine, and the ability to diagnose genetic disorders. In forensics, DNA profiling is used to identify individuals and solve crimes. In agriculture, genetic engineering has allowed for the creation of crops that are resistant to pests and diseases.
Also Read :- The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Life Sciences
DNA is the blueprint of life, holding the instructions for everything from the color of our eyes to the way our bodies function. Its role in heredity and evolution makes it a key player in the story of life on Earth. As research continues to uncover the mysteries of DNA, its impact on science, medicine, and our understanding of life will only grow.
Also Read :- Advancements in Stem Cell Therapy: Pioneering Regenerative Medicine